Parts of HVAC System: What Every Homeowner Should Know
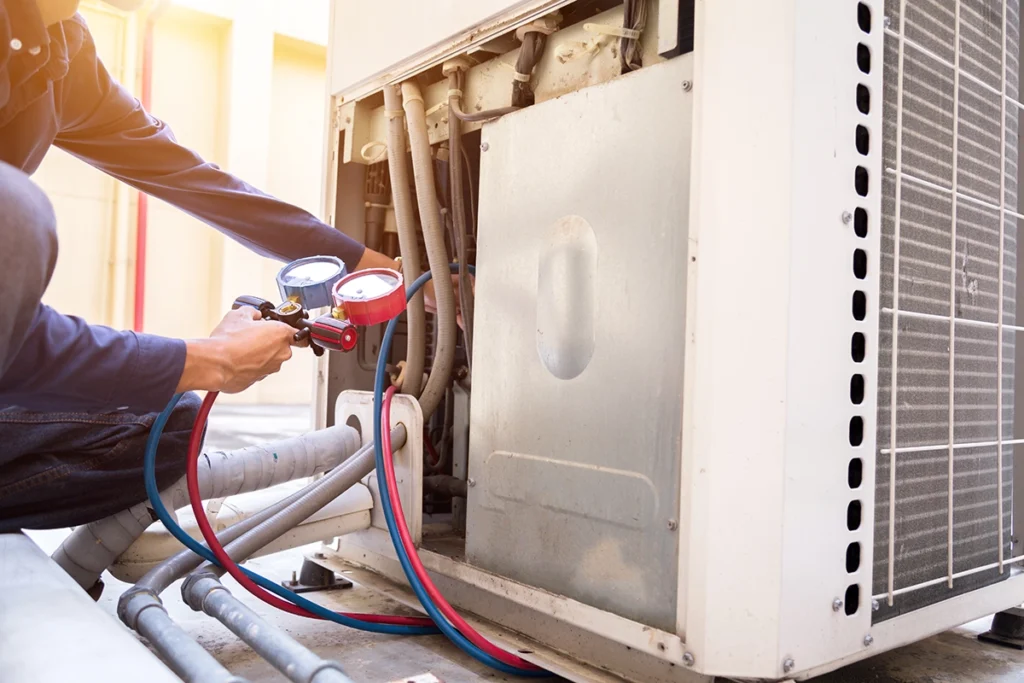
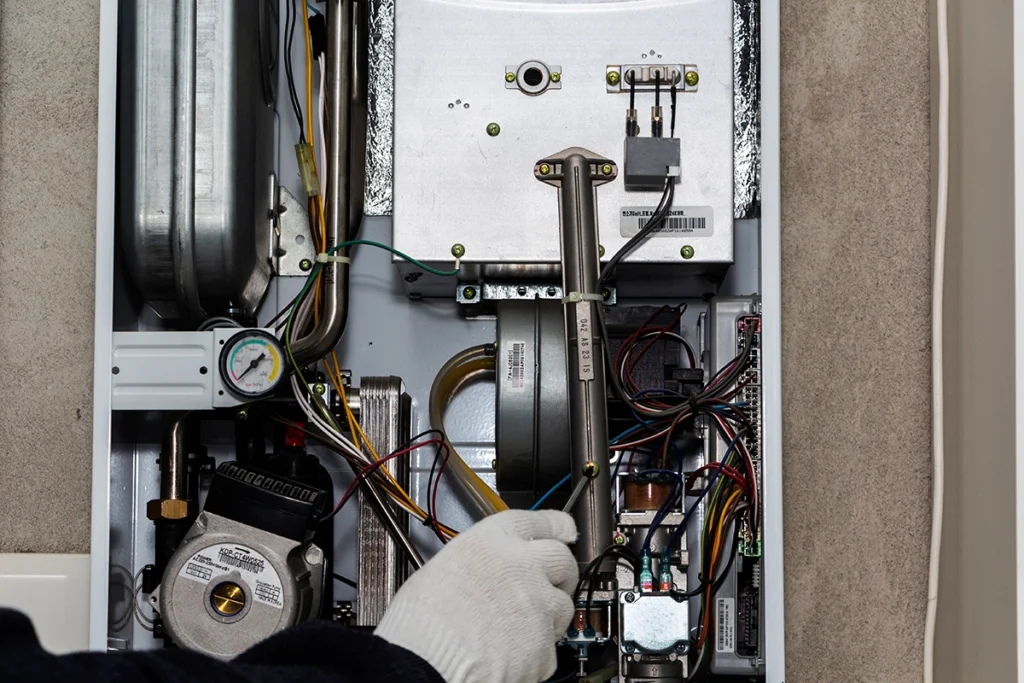
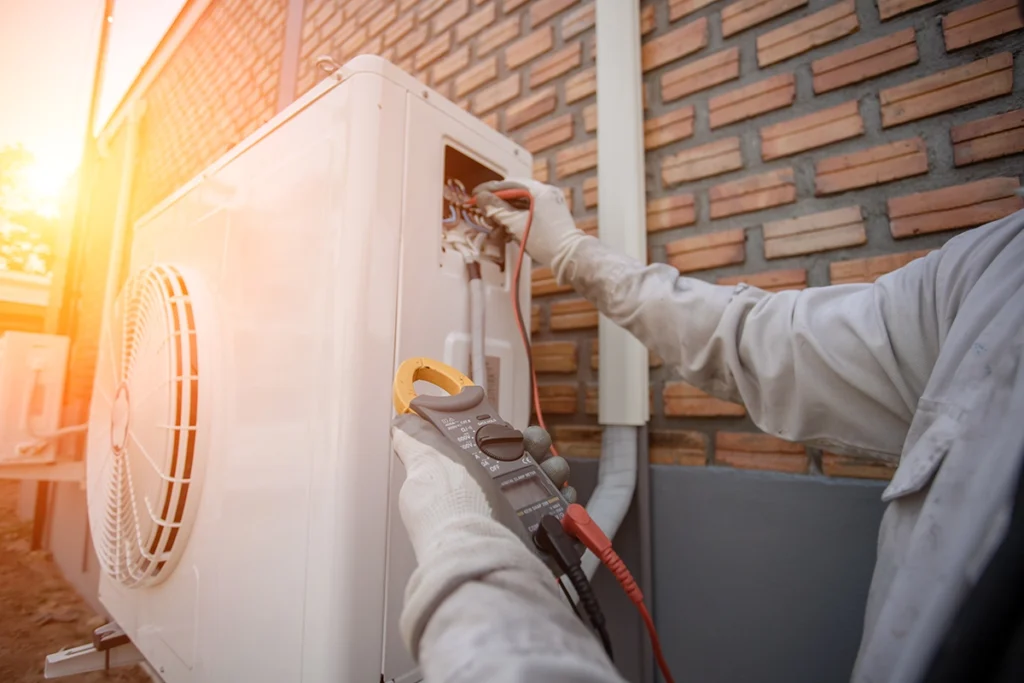
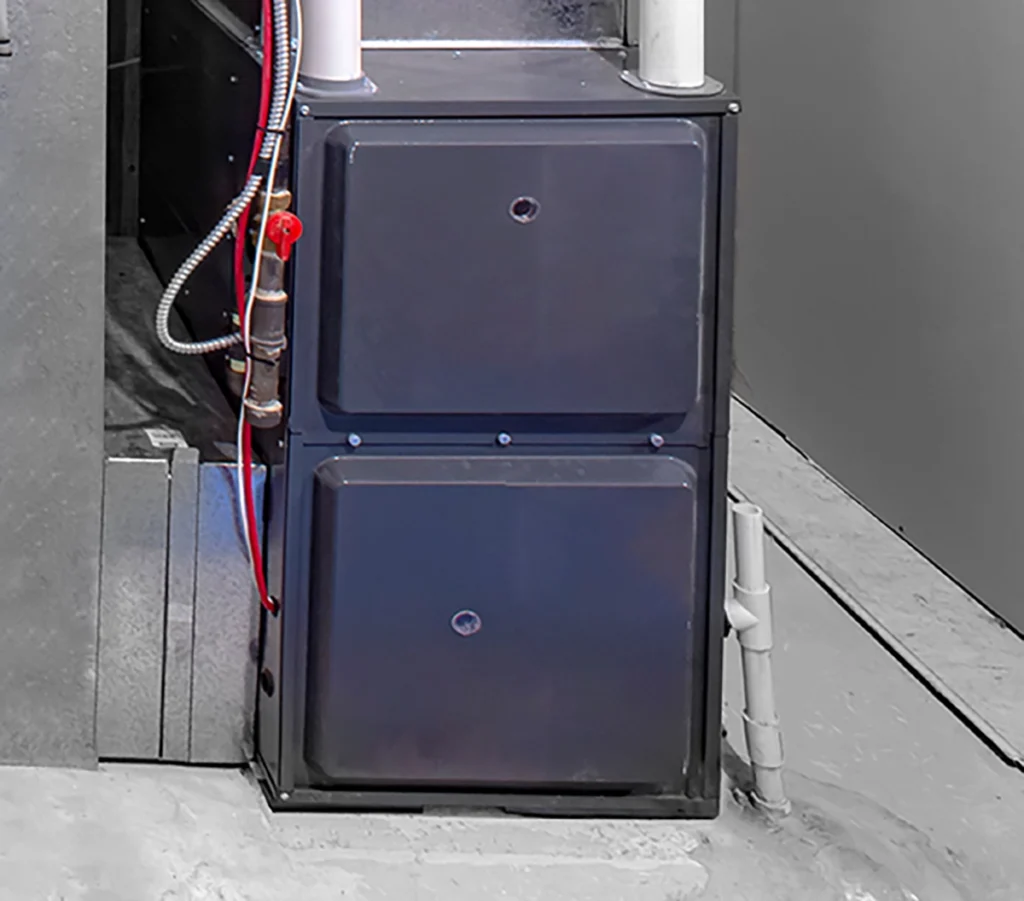
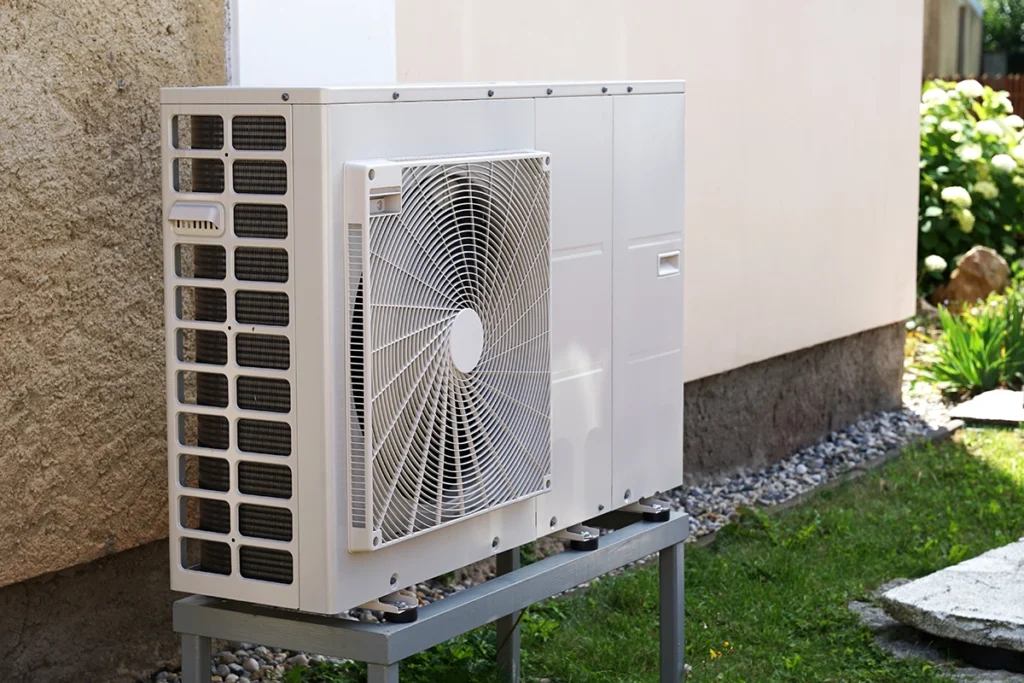
Most homeowners don’t think about the parts of HVAC system equipment until something feels off. Maybe the airflow is weaker than last month, or the temperature feels uneven from one room to the next. Since we work with heating and cooling equipment every day at C&R Services, we know how important it is to understand the essentials. When you know what each component does, you can spot issues faster and keep your home running comfortably year-round. How the Main Parts of a Forced-Air HVAC System Work Together Every home relies on the same essential HVAC components, even if the equipment varies. While systems can look different from house to house, the main parts of an HVAC system always work together in predictable ways. When one part struggles, the entire system feels the strain. Understanding those relationships helps you make smarter decisions when something breaks or when you’re planning future upgrades. Air Handlers, Blowers, and the Heart of Airflow The air handler and blower assembly control how air moves through your home. These components push conditioned air through the ducts and pull stale air back into the system. When the blower slows down, airflow drops. And as you might guess, reduced airflow often leads to hot and cold spots. If you want to understand how airflow connects to comfort, our blog on forced air heating is a good place to start because it breaks down the role of ducts, vents, and circulation in an easy way. Evaporator Coils and Condenser Coils are Key Parts of an HVAC System The evaporator coil absorbs indoor heat. The condenser coil releases that heat outdoors. These two coils perform a constant exchange whenever your cooling system runs. When dirt collects on the coils, your energy use goes up quickly. The U.S. Department of Energy explains why clean coils improve efficiency and reduce cooling cost. The Refrigerant Circuit and Why It Matters Inside the coils, refrigerant moves heat in or out of your home. Although it’s often misunderstood, refrigerant is essential for proper cooling. If the level drops, the system runs longer and temperatures start to drift. Most shortages happen because of leaks, not normal use. And when a homeowner suspects low refrigerant, they usually call us right away because refrigerant issues never fix themselves. Thermostats and HVAC System Controls Thermostats direct every other component. Yet the wrong settings or outdated technology can throw off the entire system. Smart thermostats, for example, help stabilize temperature swings and reduce wasted energy. The U.S. Department of Energy explains how updated thermostat technology improves efficiency and overall comfort, which is why proper settings matter more than most people realize. And when your thermostat isn’t communicating properly, you often feel the symptoms long before you realize the control is the problem—like short cycling, uneven temperatures, or a system that runs nonstop. Ductwork, Vents, and the Distribution Side of the System Even when the equipment runs perfectly, poorly sealed ducts leak air into unconditioned spaces. That lost air forces your HVAC system to work harder. Because the ductwork is hidden behind walls, floors, and attic spaces, it’s one of the most overlooked parts of HVAC system performance. Simple improvements like sealing joints or adding insulation can make a noticeable difference in comfort. Filters and Indoor Air Quality Air filters protect every major component. They also help maintain healthier air inside your home. When filters clog, the blower strains and the evaporator coil can freeze. Regular replacements are an easy fix, yet many homeowners forget until airflow drops. Because clean filters support airflow and reduce strain on the system, this simple, inexpensive step makes a huge difference in overall performance. Additional Parts Found in Forced-Air Heating and Cooling Systems Most homes use forced-air HVAC systems, and some setups include a few extra components depending on whether the home uses a gas furnace or a cooling system. Gas furnaces rely on burners, ignition systems, and inducer motors to create heat safely before it moves through the ducts. Cooling systems like central air conditioners and heat pumps use compressors, condenser fan motors, and condensate drains to manage refrigerant flow and moisture. Even though these parts vary by equipment type, they all work alongside the main HVAC components to keep your home comfortable. Heat Exchangers and Heating Safety Heat exchangers transfer heat from the combustion chamber to the air without mixing fumes into your living space. Because they handle high heat, they can crack over time. A cracked exchanger can allow combustion gases, including carbon monoxide, to enter the airflow, which is why annual checkups matter for safety. A damaged exchanger can also trigger safety shutdowns that keep the system from heating at all. At C&R Services, our technicians inspect these exchangers closely during seasonal tune-ups. Maintenance and Why Knowing the Parts of an HVAC System Helps When you understand the main parts of an HVAC system, it becomes much easier to spot early warning signs. Weak airflow, strange noises, short cycling, or shifting temperatures usually relate to one of the core pieces described above. And since we repair all major HVAC brands, we see how small issues turn into bigger repairs when they’re ignored. Quick action saves money and prevents breakdowns, and we provide a full range of HVAC services if you need professional support. Why Homeowners Choose C&R Services We work with HVAC systems every day, and we’ve helped families across East Texas keep their homes comfortable through long summers and chilly winter nights. If you want help, guidance, or a full system inspection, contact C&R Services and our team will be ready to help. FAQ: Quick Answers About HVAC System Parts Here are a few common questions homeowners ask when learning about HVAC components.