Mini Split Condensate Pump: What It Is and When It’s Required
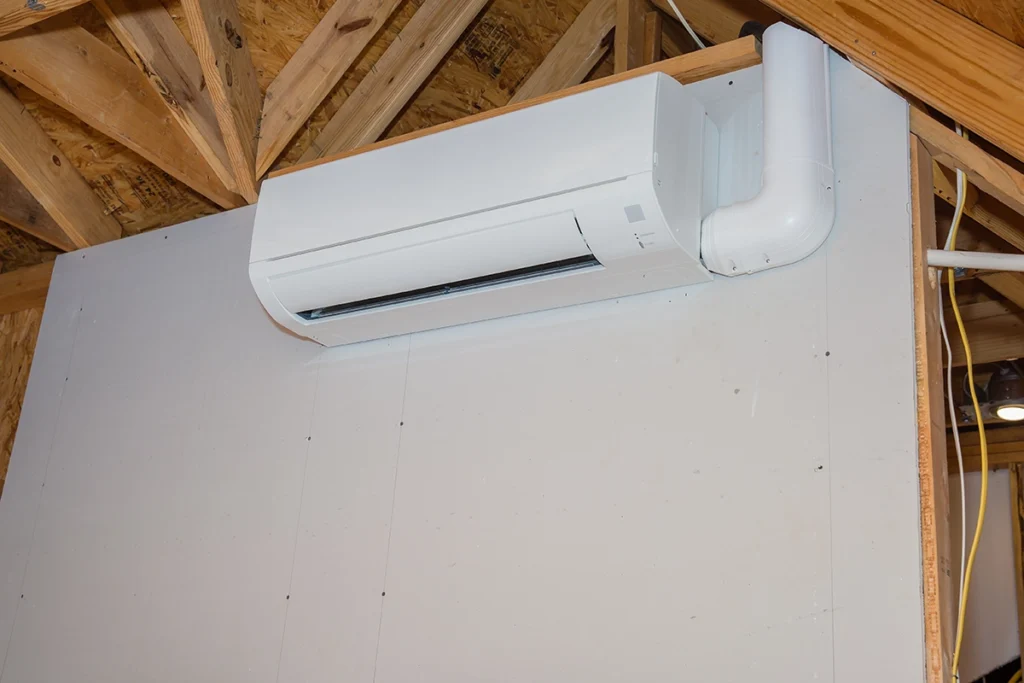
If you’re researching ductless systems, you may have come across the term mini split condensate pump and wondered whether it’s something every system needs. From our experience at C&R Services, this is one of the most common points of confusion property owners run into when learning about mini split systems. Because moisture management plays a critical role in system performance, understanding how condensate is handled helps prevent surprises later. What a Mini Split Condensate Pump Does A mini split condensate pump removes the water produced during the cooling and dehumidifying process. As warm air passes over the indoor coil, moisture condenses and must drain safely away. In many installations, gravity handles this naturally. However, when gravity drainage is not possible, a pump becomes necessary. The pump lifts condensate water upward and routes it to an approved drain location. Without proper drainage, water can back up, leak, or damage nearby surfaces. This is why industry standards emphasize proper condensate management. Guidance from the Air Conditioning Contractors of America explains that HVAC systems produce condensate during normal cooling operation, and that it must be drained or pumped to prevent water damage and system issues. When a Mini Split Condensate Pump Is Required Only some installation scenarios require a mini split condensate pump. Pumps aren’t standard on every ductless system, which often surprises property owners. You typically need a pump when: The indoor unit sits below the drain termination point The drain line must run upward at any point The unit is installed far from an exterior wall Gravity drainage cannot maintain proper slope In contrast, wall-mounted units on exterior walls often drain naturally without assistance. Because installation conditions vary widely, proper planning makes all the difference. Common Locations That Require a Pump Certain spaces frequently require a mini split condensate pump due to layout limitations. These include: Basements without floor drains Interior rooms without exterior access Garages or workshops below ground level Finished spaces with limited wall access In these situations, relying on gravity alone simply isn’t possible. How Condensation Forms in Mini Split Systems As a mini split system cools indoor air, moisture in the air condenses on the evaporator coil. That condensation collects as water and must be directed out of the system through a drain line. Without a proper drainage path, the water can back up and cause leaks, shutdowns, or performance issues. To fully understand why drainage matters, it helps to know how mini splits operate. If you’re unfamiliar with the cooling cycle, our guide explaining how mini splits work walks through the process in more detail. Mini Split Condensate Pump vs Gravity Drainage Not every mini split installation requires mechanical assistance. In many cases, gravity drainage works perfectly well. Gravity drainage works when: The drain line slopes downward continuously The exit point remains lower than the indoor unit The line stays clear and unobstructed When those conditions aren’t possible, gravity drainage can’t do the job on its own. In those cases, a mini split condensate pump helps move water out of the system safely and consistently. Maintenance Considerations for Condensate Pumps Like any mechanical component, mini split condensate pumps require routine care. Pumps can clog, fail, or trigger safety shutoffs if neglected. The Environmental Protection Agency notes that keeping HVAC drain pans clean and drain lines unobstructed helps prevent moisture problems and mold growth. Regular mini split maintenance allows technicians to clean drain lines, test pump operation, and address small issues before they affect performance. Signs a Condensate Pump May Be Failing Watch for these warning signs: Unusual buzzing or clicking sounds Water dripping from the indoor unit System shutting off unexpectedly Musty odors near the air handler These symptoms often indicate a drainage problem that won’t resolve on its own. Addressing these issues early protects both the system and the surrounding space. How Condensate Pumps Function Within HVAC Systems Although mini splits are ductless, they still include many familiar components found in traditional equipment. Understanding where drainage fits within the broader parts of an HVAC system helps clarify why condensate handling matters. Drain pans, drain lines, safety switches, and pumps work together to manage moisture within the system. When one component fails, overall performance can suffer. Are Condensate Pumps Optional or Mandatory? A mini split condensate pump isn’t always necessary. The installation setup determines if the system needs one. From our day-to-day work at C&R Services, we’ve seen systems perform flawlessly with gravity drainage, while others require pumps to operate safely. The key is proper evaluation before installation. Planning drainage correctly helps the system run better and last longer. Why Professional Assessment Matters Because every home layout differs, proper condensate drainage requires evaluation, not guesswork. Professional assessment ensures the system drains properly from day one. At C&R Services, we help property owners identify when a mini split condensate pump is needed and when simpler solutions are enough. Evaluating the mini split system before issues develop helps identify drainage needs and prevent larger problems. If you have questions or aren’t sure what your system needs, our team provides mini split services throughout Tyler and East Texas. Contact us to discuss your setup and get clear, practical advice. Frequently Asked Questions About Mini Split Condensate Pumps Below are quick answers to common questions property owners ask us. If you’re evaluating a mini split condensate pump, professional guidance ensures your system drains safely and efficiently.