What Is Auxiliary Heat and How Does It Work?
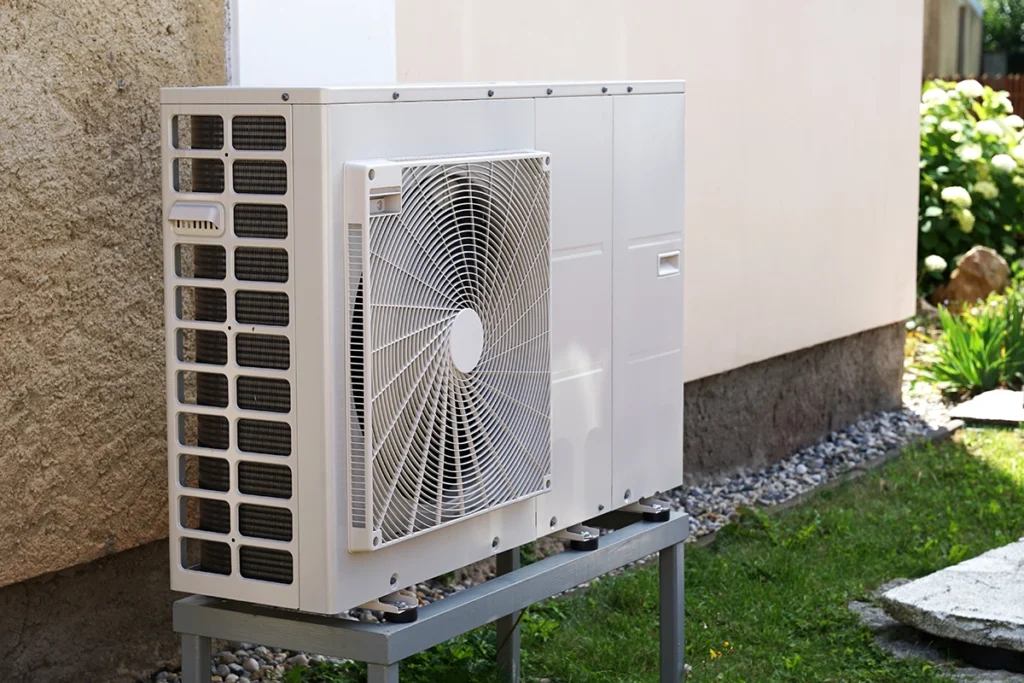
When homeowners ask “what is auxiliary heat,” it usually comes up on the first cold morning when their thermostat suddenly flashes “AUX.” You might wonder — is something wrong with my heat pump, or is this normal? At C&R Services, we’ve had plenty of calls that start with that same question. The short answer: it’s not always bad news. Auxiliary heat is simply your system’s backup plan for extreme weather, helping your home stay warm when your heat pump can’t keep up on its own. What Is Auxiliary Heat in a Heat Pump System? In simple terms, auxiliary heat (or “aux heat”) is a secondary heating source that kicks on automatically when your heat pump needs extra help. During mild weather, your heat pump transfers heat from outside air into your home. But when temperatures drop below a certain point — usually around 35°F to 40°F — that process becomes less efficient. That’s when auxiliary heat steps in. It usually uses electric resistance coils or, in some setups, a gas furnace to supply additional warmth. You might think of it like a car’s turbo boost — it’s not always running, but when it is, it gets the job done quickly. Many homeowners confuse auxiliary heat with emergency heat (EM heat) since both appear on thermostats and both provide backup warmth. The key difference is that EM heat must be turned on manually, while aux heat activates automatically when the system senses it needs extra power. For a deeper comparison, check out our post on what EM heat is and when you should use it — it explains when that mode should (and shouldn’t) be used. When Does Auxiliary Heat Turn On? Your thermostat and system controls decide when auxiliary heat activates. You might notice “AUX” appear on the display if: Outdoor temperatures are too cold for your heat pump to work efficiently Your thermostat raises the temperature several degrees at once The heat pump goes into defrost mode and needs temporary backup heat In most cases, auxiliary heat turns off automatically once your home reaches the set temperature. Still, if you see “AUX” on all the time, that can mean your system is struggling to keep up — or that something needs professional attention. (We’ve seen plenty of situations where a simple thermostat setting caused unnecessary aux use.) The Cost of Running Aux Heat Here’s the part homeowners often don’t love hearing: auxiliary heat uses more energy than regular heat pump operation. That’s because electric resistance coils draw a lot of power. If your system relies on auxiliary heat too often, your utility bills can climb fast. To keep costs down, make sure your home is properly insulated and sealed. Also, avoid large temperature swings on your thermostat. Gradual adjustments give your heat pump time to do most of the work before aux heat is needed. For more details on heat pump efficiency, the U.S. Department of Energy offers great guidance on how to optimize your system for different climates. How to Tell If Auxiliary Heat Is Working Properly One quick test is to check how the air feels. When auxiliary heat activates, supply air from your vents should feel noticeably warmer than during standard heat pump operation. If it feels cold or only slightly warm, there could be an issue with the heating elements or thermostat settings. At C&R Services, we test for this during regular maintenance. We measure current draw, inspect relays, and verify thermostat communication — small details that can make a big difference when temperatures drop. Preventing Overuse of Aux Heat 1. Regular MaintenanceA clean, tuned-up system performs better and doesn’t rely on backup heat as often. Dirty coils, clogged filters, or low refrigerant levels can all cause your heat pump to struggle. 2. Smart Thermostat SettingsModern thermostats can learn your habits and reduce unnecessary aux usage. (We’ve seen some homeowners cut energy use by 10–15% just by upgrading.) 3. Weather AwarenessWhen severe cold hits, it’s normal for auxiliary heat to run more often. But if you live in an area with frequent temperature dips — like parts of East Texas in January — it’s worth having a technician review your setup to ensure efficiency. If you’re looking for reliable seasonal advice and ways to save on heating costs, ENERGY STAR’s Heating and Cooling Guide has some solid, easy tips to follow. When to Call a Professional If your system runs on auxiliary heat constantly, blows cold air, or shows unusually high energy bills, it’s time for a service call. For more insight on that cold air issue, check out our post on why your heater might be blowing cold air — it breaks down the common causes and what to check before calling a pro. At C&R Services, we specialize in diagnosing all types of heat pump issues — including auxiliary heat problems — with accuracy and care. Whether you need repairs, maintenance, or a full system check, we’re here to help keep your home comfortable. FAQs About Auxiliary Heat Now that we’ve covered the basics, here are some common questions we hear about auxiliary heat during service calls. If you’ve ever wondered about aux heat and how it affects your comfort, the key takeaway is that it’s your system’s safety net — helpful when needed, but costly if overused. For peace of mind and optimal performance, schedule a heat pump inspection with C&R Services today. Contact C&R Services to learn more about our heat pump services or to book a professional tune-up that keeps your system running efficiently all winter long.