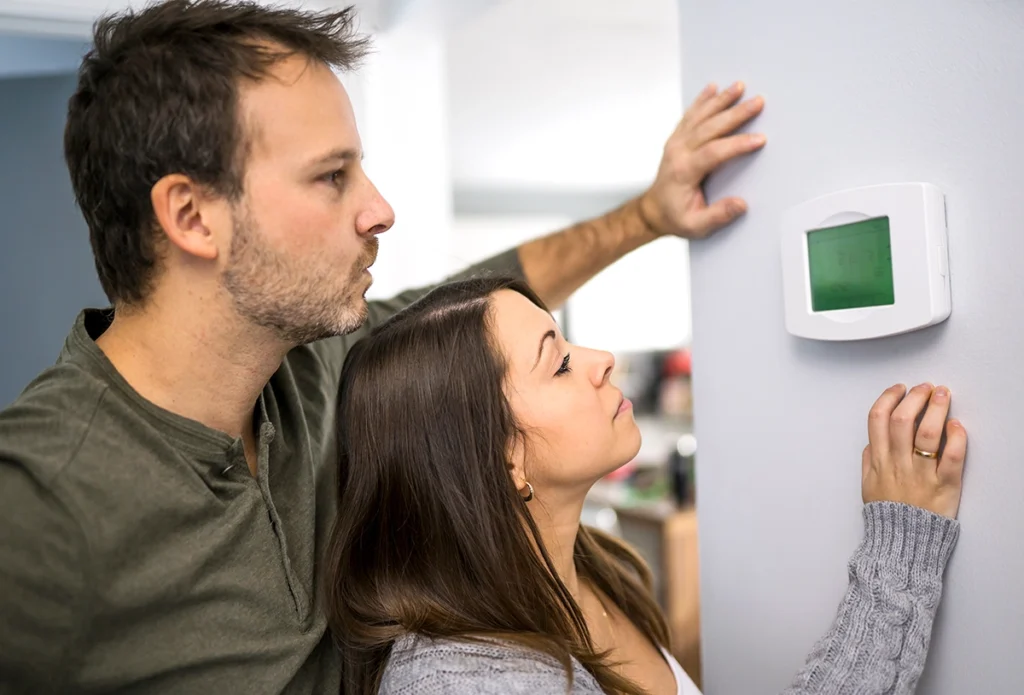
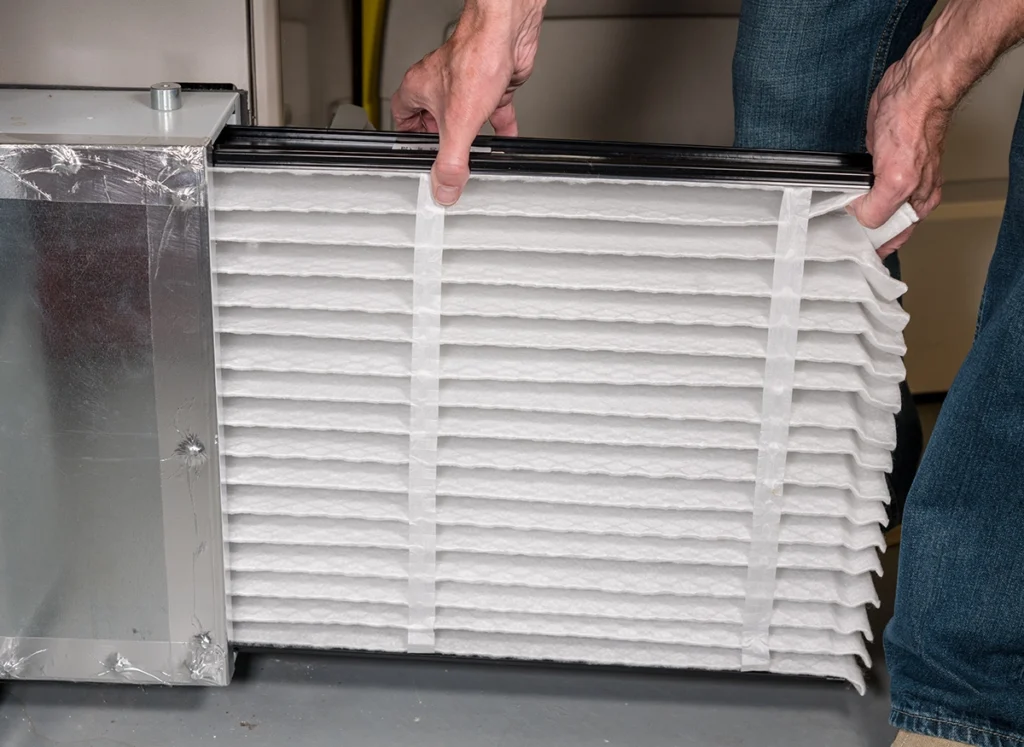
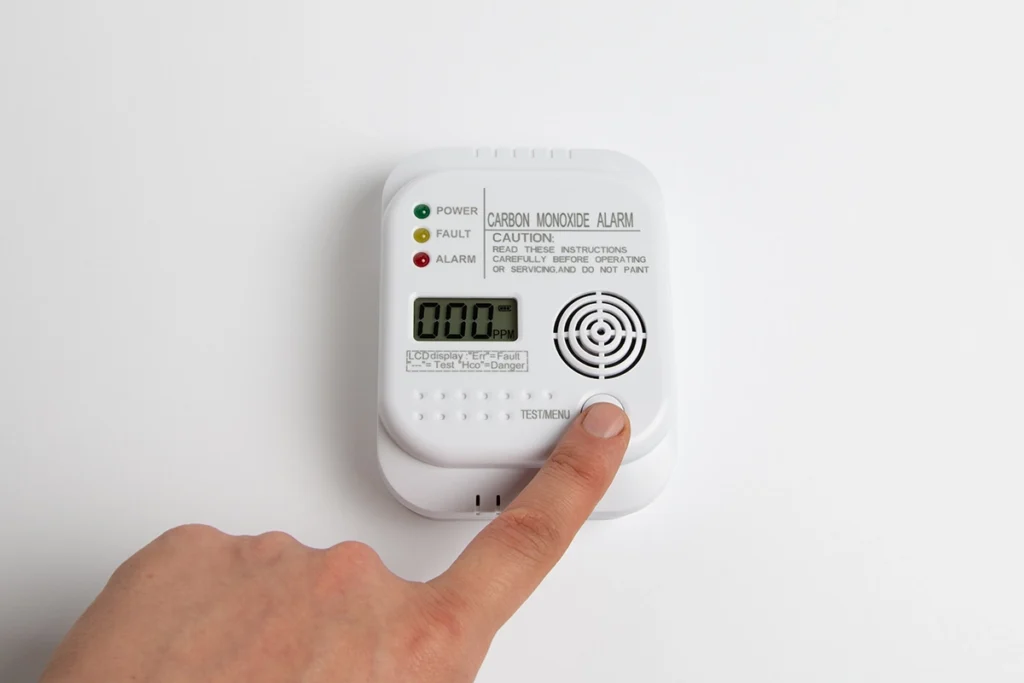
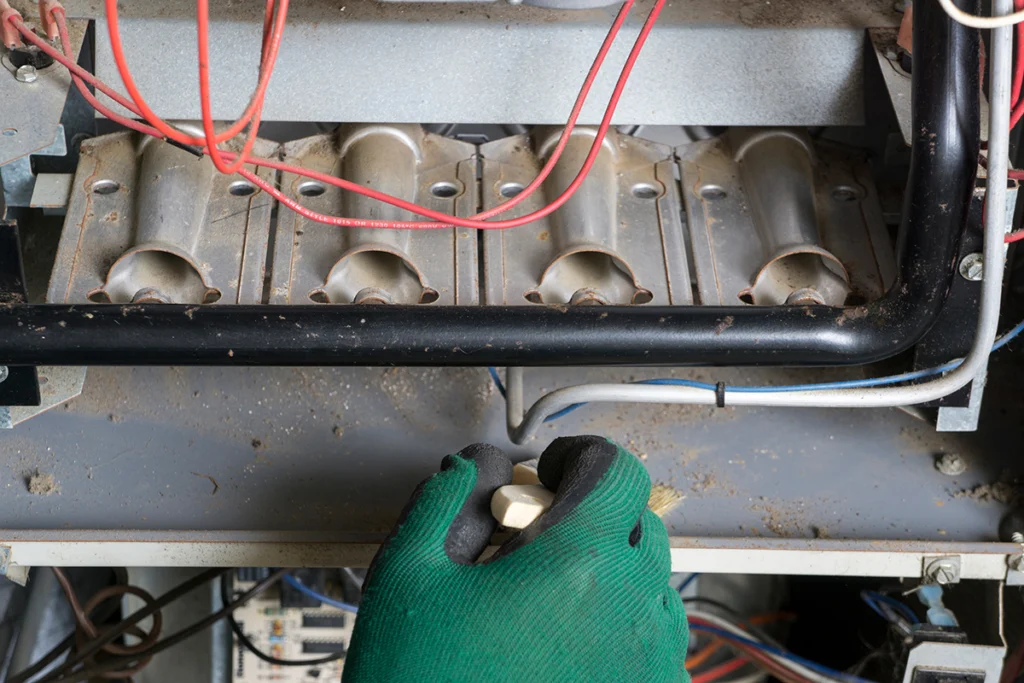
Heater Not Working? Why Your Heat Isn’t Turning On
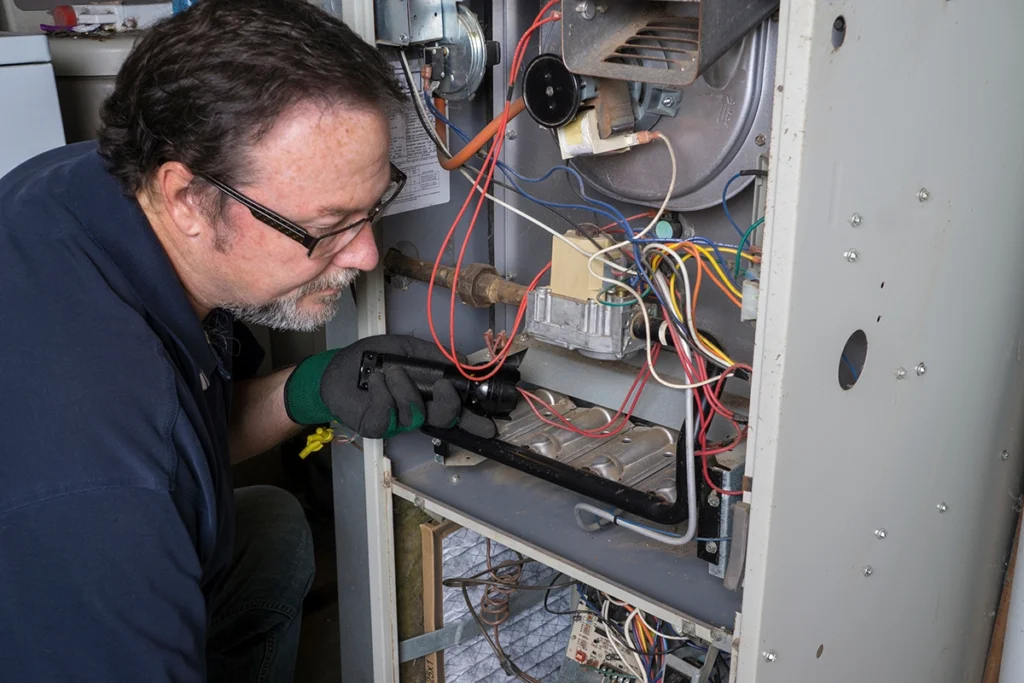
Winter service calls usually start the same way — with a heater not working and a house that’s getting colder by the hour. Sometimes the system won’t turn on. Other times, it runs nonstop but never produces heat. Either way, the stress adds up quickly. From our day-to-day work at C&R Services, we’ve learned that most heating problems follow predictable patterns once you know what to look for. Fortunately, a heater not working doesn’t always mean a major breakdown. In many cases, the issue starts with airflow, controls, or built-in safety devices. Knowing how these systems behave can help you tell what’s normal, what’s not, and when professional heating repair makes sense. When a Heater Isn’t Working at All When a heater won’t turn on at all, we begin by confirming the system can actually start a heating cycle. Power interruptions, tripped breakers, or fuel supply issues can stop heating before it ever gets going. These problems are easy to miss, yet they account for a surprising number of winter service calls. If power and fuel are present, we shift our focus to the system’s controls and safety logic. Modern heating equipment won’t start if it senses a condition that could cause damage or unsafe operation. In many cases, the heater is being prevented from turning on—not because it’s broken, but because a control or safety component is doing its job. When that protection keeps activating, further diagnosis is needed. Heater Not Working but the System Is Running In some situations, the heating system turns on and stays running, but the house never gets warmer. You may hear the blower operating, feel air moving through the vents, and assume heat should follow. Instead, the temperature stays flat. This usually means the system is starting a cycle but can’t complete it. Problems with airflow, ignition, or internal heat transfer can stop heat from being produced or delivered, even though the system appears active. When that happens, the heater may run longer than normal while never actually warming the living space. Heater Blowing Cold Air Instead of Heat One symptom we see frequently is a heater blowing cold air. While that can feel alarming, it isn’t always dangerous. For example, furnaces sometimes blow cool air briefly before warming up. However, ongoing cold airflow usually signals a problem that needs attention. In many service calls, we find dirty filters, overheating protection, or ignition failures behind the issue. If the air never warms up, learning what causes a heater to blow cold air can help you decide whether it’s normal behavior or time to call for service. Heater Not Working Because of Thermostat Issues Before assuming equipment failure, thermostat operation deserves attention. A heater not working complaint often traces back to incorrect settings, dead batteries, or wiring problems at the thermostat. Because thermostats control when heating cycles begin and end, even minor issues can stop heat completely. We often help homeowners understand what happens when a thermostat isn’t working correctly, since fixing control problems early can restore heat without deeper repairs. Safety Devices That Can Stop Heat Suddenly Modern heating systems include safety components designed to shut things down when conditions become unsafe. While these protections are critical, they can also cause confusion when a heater not working situation appears without warning. One common example is overheating protection. When internal temperatures rise too high, the system shuts off automatically. This often relates to airflow restrictions or mechanical wear. Learning how a furnace limit switch shuts down heating to prevent damage helps explain why heat may stop even when nothing appears broken. When Safety Shutdowns Point to Bigger Issues In more serious cases, repeated shutdowns point to underlying problems that affect safe operation. Components like the heat exchanger play a critical role in transferring heat while keeping combustion gases contained. When damage occurs, the system may shut down repeatedly or stop heating altogether. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, each year more than 400 Americans die from unintentional carbon monoxide poisoning not linked to fires, with more than 100,000 emergency department visits and over 14,000 hospitalizations tied to CO exposure. Because of that risk, any heater not working issue paired with unusual odors, alarms, or repeated shutdowns should be addressed immediately. Why Professional Heating Repair Matters Although some heating issues are simple, others require professional tools and diagnostics. At C&R Services, we focus on identifying the root cause instead of applying temporary fixes. A trained technician can safely evaluate controls, combustion, airflow, and safety systems together. If your heater isn’t working consistently, professional service helps prevent repeated shutdowns and protects long-term system health. What Homeowners Can Check Before Calling While not every heating issue is DIY-friendly, a few quick checks can often help clarify why heat isn’t coming through the system. Start by confirming the thermostat has power and is set correctly. Then, check the air filter for dirt or blockage. Closed or obstructed vents can also restrict airflow and prevent warm air from circulating through the house. Finally, listen for unusual startup noises, which can signal an internal issue. Airflow problems are one of the most common reasons a heater struggles to warm a home. According to ENERGY STAR, airflow issues can reduce a heating system’s energy efficiency by up to 15 percent, which often leads to uneven temperatures or repeated shutdowns during winter operation. If heat still doesn’t return after these checks, delaying service often leads to larger repairs and longer downtime. When to Call C&R Services When your heater isn’t working and your home is getting colder, fast answers matter. Our team helps homeowners understand what’s happening and what steps restore heat safely. We work with furnaces, heat pumps, and electric systems, so issues don’t get overlooked. If you’re in Tyler or East Texas and your heat isn’t working, contact C&R Services to schedule service. Our technicians provide professional heating repair to restore comfort quickly and safely. Frequently Asked Questions When the Heat Stops Working Heating problems raise