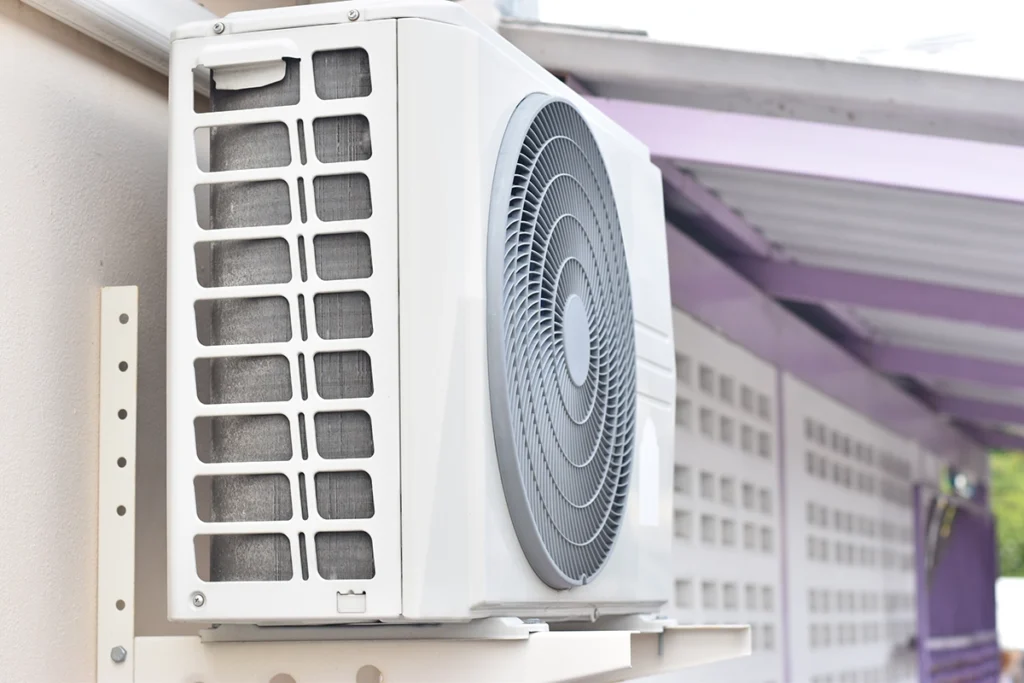
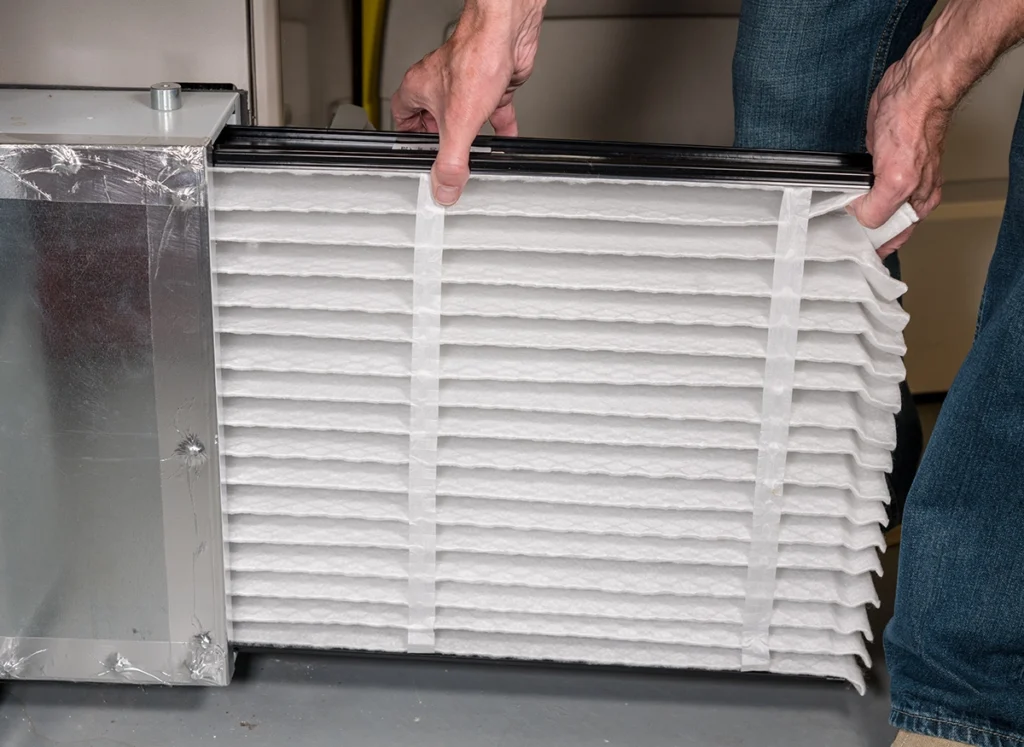
Disadvantages of Mini Split Systems Explained
If you’re researching modern heating and cooling options, you’ve probably come across ductless systems. While they’re popular, the disadvantages of mini split systems deserve just as much attention as the benefits. From our day-to-day work at C&R Services, we’ve seen property owners surprised by certain limitations after installation. Because of that, understanding the downsides upfront helps you make a confident, informed decision. Mini splits absolutely have their place. However, like any HVAC system, they aren’t a perfect fit for every home or situation. Below, we break down the most common drawbacks, based on real-world experience, not sales hype. Disadvantages of Mini Split Systems Compared to Traditional HVAC One of the first disadvantages people notice is how different mini splits feel compared to conventional systems. Mini splits condition individual rooms instead of the entire home or building at once. While that zoning sounds appealing, it can also create uneven comfort, especially in larger or multi-room spaces. For example, one room may feel perfect while another lags behind. In contrast, central systems distribute air more evenly throughout the entire space. This difference becomes clearer when you compare mini splits to ducted options. That’s why we often recommend learning how traditional setups work, especially when comparing alternatives like forced air heating and how it handles whole-home comfort. Higher Upfront Costs Are a Common Disadvantage of Mini Split Systems Another one of the major disadvantages of mini split systems is cost. While they can save energy over time, installation often costs more upfront. Each indoor unit adds expense. Larger homes may require several units to cover all living spaces. As a result, total installation costs can exceed expectations quickly. In small commercial spaces, costs can scale faster when multiple rooms or zones need independent control. Additionally, electrical upgrades are sometimes required. Older homes may not have the capacity needed to support multiple indoor units. That extra work adds both time and expense to the project. Disadvantages of Mini Split Systems When It Comes to Sizing Sizing errors are more common with ductless systems than many people realize. Unlike central systems, each indoor unit must be sized correctly for its specific space. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, ductless mini-split systems require careful sizing and placement to avoid efficiency losses and comfort problems. If a unit is too small, it struggles to keep up. If it’s too large, it short cycles and wastes energy. Both scenarios reduce comfort and efficiency. Because of that, we often guide people to learn more about sizing basics. Understanding what size mini split you need can prevent one of the most common disadvantages of mini splits. Why Improper Sizing Causes Long-Term Problems Improper sizing doesn’t just affect comfort. Over time, it also increases wear on the system. Short cycling strains internal components. Meanwhile, undersized units run constantly. Both situations shorten system lifespan and increase repair risks. From our experience at C&R Services, many performance complaints trace back to sizing mistakes made early on. Visual Impact Another commonly overlooked disadvantage of mini split systems is appearance. Wall-mounted indoor units remain visible at all times. Some people dislike how units interrupt décor or wall space. This concern becomes more noticeable in living rooms, bedrooms, historic homes, or customer-facing commercial spaces. Although there are ceiling and concealed options, those designs increase cost and complexity. As a result, aesthetics become a deciding factor for many property owners. Maintenance-Related Disadvantages of Mini Splits Mini splits still require regular maintenance. Filters need frequent cleaning, often more than many people expect. Because each indoor unit has its own filter, maintenance tasks multiply quickly. When filters clog, airflow drops and efficiency suffers. Additionally, professional service can be more specialized. Not every technician is equally experienced with ductless systems. That can affect repair timelines and costs. Cold Weather Performance Can Be a Disadvantage Although cold-climate models exist, performance can still drop in extreme conditions. In colder regions, backup heat may be required. That added system complexity surprises some property owners. While technology has improved, climate still plays a role in overall satisfaction. ENERGY STAR explains that ductless mini-split heat pumps can deliver efficient heating and cooling year-round, but real-world performance depends on system design, climate, and installation quality. Disadvantages of Mini Split Systems for Whole-Home Air Quality Mini splits don’t use ductwork. While that reduces duct losses, it also limits whole-home filtration. Central systems often integrate advanced air cleaners, humidifiers, or UV systems. Mini splits usually condition air locally without treating the entire home. For those prioritizing indoor air quality, this limitation matters. It’s one reason some households prefer traditional HVAC designs. Are the Disadvantages of Mini Split Systems a Dealbreaker? Not always. For many homes, mini splits are an excellent solution. However, understanding the disadvantages of mini split systems ensures expectations stay realistic. At C&R Services, we believe the right system depends on the home, the budget, and long-term goals. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Our heat pump services help property owners compare ductless and traditional systems, review sizing considerations, and understand long-term performance before making a decision. A quick conversation often helps clarify expectations before moving forward. That kind of guidance matters, especially near the end of your research. If you need honest input, contact C&R Services for straightforward advice and clear answers. We proudly serve Tyler and East Texas, and we’re always ready to help property owners choose systems that truly fit their needs. Frequently Asked Questions About Mini Splits Before wrapping up, here are a few quick answers we commonly share. If you’re still evaluating the disadvantages of mini split systems, a professional consultation helps clarify what works best for your home.